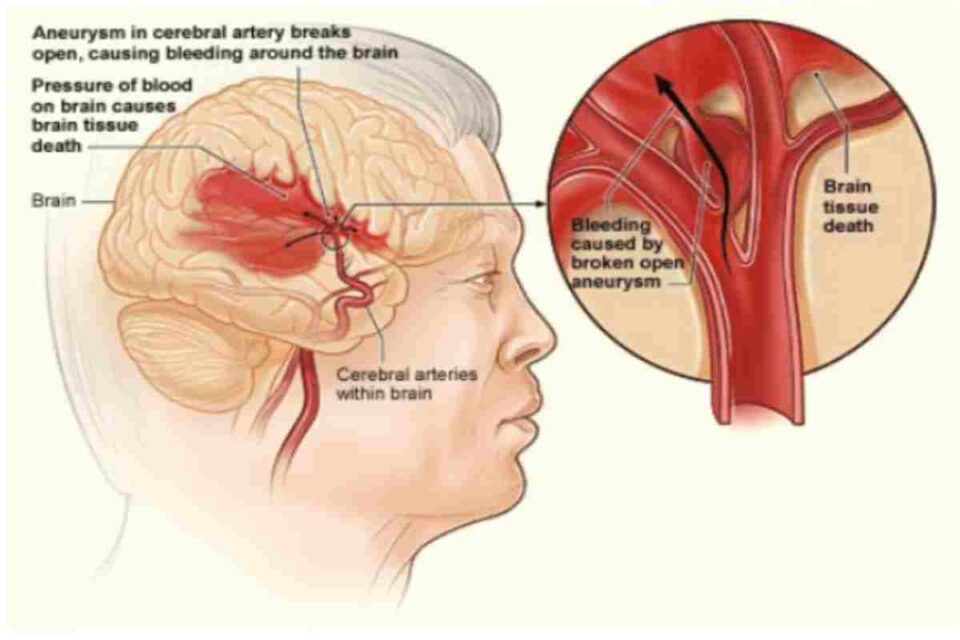
Blood Disorders That Lead to Stroke: A stroke is brain damage caused by the disruption of blood flow to the brain. This often results from restricting normal, smooth blood flow due to damaged blood vessels in the brain, heart, or neck. Blood vessels are damaged due to long-term problems such as smoking, diabetes, and hypertension. In addition, high cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood tend to adhere to the wall of the arteries, which causes the narrowing of these blood vessels and predisposes to the formation of harmful blood clots that interrupt blood flow in the brain and cause a stroke.
Most of the blood disorders that lead to the course are hereditary, and medications cause some. However, sometimes a defect involving a person’s blood is the cause of a stroke. Blood clotting diseases make a person more likely to form harmful blood clots, which cause ischemic strokes. Bleeding disorders cause extreme bleeding, which can lead to hemorrhagic strokes. However, life after a stroke can be possible Learn more about the most common blood disorders that lead to the course.
Table of Contents
Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease is one of the most significant common inherited blood disorders. It is a disease that causes a condition called ‘sickness’ of red blood cells. The disease is when a red blood cell suddenly changes from its standard, rounded shape and turns into an unusual, irregular shape.
When somebody with sickle cell disease has a disease or infection, this can trigger a sickle cell crisis in which red blood cells talk and form blood clots.
People with sickle cell disease are 2-3 times more likely to suffer a stroke than people who do not have sickle cell disease. In addition, a person with sickle cell disease is more likely to have a stroke at a younger age than persons who do not have sickle cell disease.
Most people with sickle cell disease are diagnosed during childhood and are usually aware that they have the disease years before suffering a stroke.
If you have sickle cell disease, the most effective way to prevent a stroke is to prevent a sickle cell crisis, a lifelong challenge.
The cellular disease is an inherited disease. It is an X-related recessive disorder. If a person has an X chromosome that encodes the illness and another X chromosome that does not encode the condition, the individual is not expected to have the disease. Since males have one X chromosome, the young would have the situation if the X chromosome codes for sickle cell disease. On the other hand, a female takes two X chromosomes, so if one of her X chromosomes encodes sickle cell disease and the other X chromosome does not encode the disease, the woman will not have the full effects of the disease.
Blood Cloning and Protein Abnormalities
Blood clotting is a complex physiological response to bleeding. When you have an injury, your body forms blood clots to prevent blood loss. For example, whenever you have an open cut, the body makes a blood clot to stop the bleeding. This requires several proteins and hormones that act pretty quickly. Sometimes the proteins involved in making blood clots can overreact or underestimate.
This is regularly due to one of the genetic disorders of the blood.
The most common genetic diseases that cause excessive blood clot formation include the following:
- Acquired hyperhomocysteinemia
- Protein C or S deficiency
- Factor V Leiden mutation
- Methyl tetrahydro-folate reductase (MTHFR)
- C677T mutation
- Anticardiolipin antibodies
- Anticoagulant wolf
- Thrombocytosis
- Prothrombin gene mutation G20210A
- Fibrinogen, factor XIII gene abnormality
All of these blood clotting problems are rare. However, when someone has an unexplained stroke without an obvious risk factor, especially when the person is young, blood clotting disorder can cause the stroke.
Most regular medical labs are not equipped for the specialized tests involved with these diseases, and test results for blood clotting diseases often take a long time to return. Many of these blood clotting disorders are familiar, so as part of the evaluation of these rare blood clotting diseases, your doctor may ask if you have a family history of unusual blood clots or if you have circulation problems.
Bleeding Problems
Bleeding problems make it difficult for your body to create a healthy blood clot. If you obtain a bleeding disorder, you may bleed longer than expected after getting a cut. Some of the blood disorders that cause excessive bleeding are called hemophilia. Bleeding in the brain is a rare complication of some useless bleeding disorders. These disorders are characterized by a deficiency in one or more proteins the body needs to form a healthy blood clot.
Hemorrhagic deficiencies associated with hemorrhagic stroke include severe FV, FX, FVII, and FXIII deficiencies. It is rare to have one of these bleeding problems, and even among people who have these diseases, it is rare to have a hemorrhagic stroke. Hemorrhagic may request tests for o
Also read: Prostate Cancer Through Robotic Surgery
Cancer
Cancer affects the body in several ways. One such method is by making the blood more prone to forming excessive blood clots. People with cancer are prone to blood clots that can cause pulmonary embolism and stroke. People with cancer have about a 20 percent risk of stroke. This may be a consequence of chemotherapy, but cancer itself can make the body more likely to take a course.
It is rare for someone who has cancer to have a stroke before diagnosing cancer. However, when someone has an unexplained stroke, the medical team can test for cancer to see if that could explain the unexplained stroke. If you have an unexplained stroke, often called a cryptogenic stroke, you may have several blood tests to realize a medical cause for the cryptogenic stroke, such as a blood disorder or cancer.
Side Effects on Blood Thinning
Bleeding is one of the greatest common side effects of blood thinners . Although it is not uncommon for blood thinners to cause bleeding in the brain, it can occur as a complication of blood thinners. This is known a hemorrhagic stroke and is more likely to occur when the dose of a blood extender is too high. Blood thinners are treated that are used to stop blood clots.
Hormone Therapy
Birth control pills and estrogen-based or testosterone-based hormone replacement therapy have been associated with increased blood clot changes, including strokes. The risk of suffering a stroke due to birth control pills is relatively low, although the combination of smoking and birth control increases that risk. The relationship between hormone replacement therapy and stroke is quite complicated. You can find more information about the link between stroke and the most common hormones, such as estrogen, erythropoietin, and testosterone.
Overdose of Vitamins or Herbs
Some vitamins and herbs can affect blood clotting, which causes an ischemic stroke or a hemorrhagic stroke. Vitamin K, a natural component of green leafy vegetables, helps normal, healthy blood clotting. Overdose of vitamin K, through the use of pills or injections, can cause dangerous blood clots. Some herbs like ginger and ginger can cause an excess of blood weakness, especially in people who already take blood thinners like aspirin. It is best to stay in moderation when taking vitamins and herbs. You can find out more about how vitamins and herbs affect the brain.