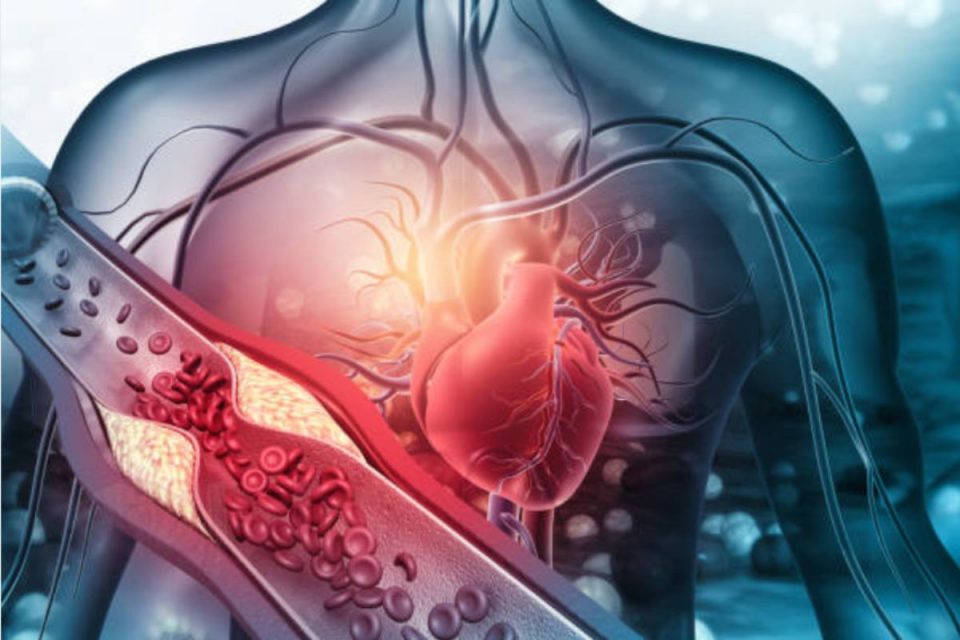
What is Cholesterol?: Cholesterol is a sterol (lipid or fat) that the human body needs to function correctly. Still, too much in the blood is wrong because it can lead to heart disease and stroke, among other problems.
The medical term for high cholesterol levels is lipid disorder, dyslipidemia, hyperlipidemia, or hypercholesterolemia.
There are many types of cholesterol, the most common of which are:
- Total cholesterol: a combination of all cholesterols
- High-density lipoprotein – often called “good” cholesterol
- Low-density lipoprotein – Often called “bad” cholesterol.
Table of Contents
What Symptoms Does it Present?
The cholesterol level usually increases with age. Although it does not usually produce symptoms, it only detected with a blood test.
Causes of Cholesterol
People with a family history who are overweight or consume many high-fat foods are very prone to high cholesterol levels. Other risk factors can be diabetes, kidney disease, or polycystic ovary syndrome, among others.
Can it be Prevented?
You can lower your LDL by exercising and eating fruits and vegetables.
What Does the Treatment Consist of?
The best treatment for LDL, is to adopt healthy habits, such as:
- No Smoking
- Eat low-fat sauces
- Avoid foods that have a lot of saturated fat (see diet for cholesterol ).
- Exercise
- Losing weight, in case of overload
Learn to Control Bad Cholesterol (LDL) Levels
There are two ways to control LDL, also known as bad cholesterol: eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly.
But these measures are not enough. Therefore, it recommended to combine them with pharmacological treatment, always taking into account the profile and needs of each patient.
However, we must know that medication, by itself, will never be enough to regulate cholesterol. You can control risk factors such as hypertension, being overweight, obesity, diabetes, and blood clotting. This may make it necessary for those dealing with high cholesterol to have to look for overweight life insurance rather than a typical term policy
For this reason, it is worth stopping and knowing what the ” Changes in your Lifestyle ” (CEV) program consists of. As we have already advanced, the first factor is to follow a balanced diet. The main goal is to decrease saturated fat and increase soluble fiber.
CEV: Dietary Changes to Regulate Cholesterol Levels
Reducing the consumption of saturated fat to less than 9% of calories will mean a decrease in LDL-C levels of between 8-10%, and supplementing this loss with an increase of 5-10g per day of soluble fiber would mean, also, the 3-5% reduction of high cholesterol.
Following a balanced diet is essential to reduce and triglycerides and avoid atherosclerosis.
The second factor, regular physical activity, goes further and aims to accelerate the effects of the diet and adopt the changes in an easier way.
For example, throughout the first three months of action, the goal will be to reduce LDL-C levels and achieve this by following a healthy diet and doing physical exercise.
Weight loss represents fundamental values in high levels. Losing between 4-5kg means reducing LDL by 5-8%.
What Foods Help Lower LDL Cholesterol Levels?
The most effective strategy to achieve this is to reduce caloric intake and, at the same time, increase physical activity.
Here are three food groups that help achieve this:
- Recommended foods: fruits, vegetables, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, fish, and olive oil. They are low in saturated fat and high in carbohydrates and plant fiber and should consume regularly.
- Foods to consume in moderation: lean meat and seed oils. They contain much-unsaturated fat or moderate amounts of saturated fat, so their daily consumption not recommended.
- Not recommended foods: includes industrial pastries, whole dairy products and derivatives, butter, fatty meats, cold cuts, and commercially fried foods. As far as possible, it is suitable to avoid them or consume them promptly, since they contain much-saturated fat.
Following this dietary guideline will help us improve our cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of cancer or diabetes.