Table of Contents
Introduction
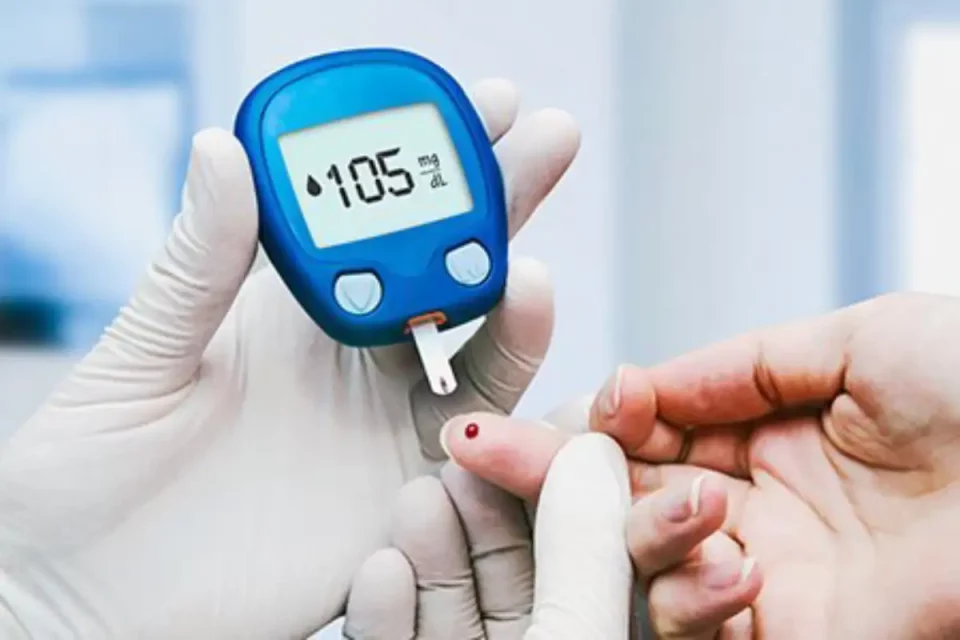
Diabetes – Symptoms, Causes, and & Treatment – Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects the way the body handles sugar. Symptoms of [diabetes] include frequent urination, thirst, and hunger. If someone has these symptoms without other medical conditions, they should see their doctor.
[Diabetes] is a chronic (long-lasting) health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. Your body breaks down most of the food into sugar (glucose) and releases it into your bloodstream. When your blood sugar goes up, your pancreas releases insulin.
[Diabetes] is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces.
If you have any of the following diabetes symptoms, see your doctor about getting your blood sugar tested:
- Urinate (pee) a lot, often at night.
- Are very thirsty.
- Lose weight without trying.
- Are very hungry.
- Have a blurry vision.
- Have numb or tingling hands or feet.
- Feel very tired.
- Have very dry skin.
Types of [Diabetes]
There are two major types of diabetes: type 1 vs. type 2. Type 1 is an autoimmune condition where your immune system destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
With type 2, either your pancreas makes little or no insulin, or you have become resistant to its effects on glucose metabolism. Therefore, it takes longer for blood sugar levels to return after eating food than for people without diabetes. Type 2 diabetes also increases the risk of developing health complications like blindness, kidney disease, heart disease, and nerve damage.
People with diabetes need to closely monitor their blood sugar levels to prevent these long-term complications from occurring or worsening. An effective way to manage diabetes is through good self-care habits such as eating healthy food regularly throughout the day.
Causes
There are many possible causes of diabetes. These are genetics, obesity, and not exercising enough or at all. The following increase your risk for type-two diabetes:
- Having a family history of the disease
- Being overweight
- Not getting any physical activity
- Living with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or a history of heart disease
There are also some rarer causes of [diabetes], such as:
- Gestational diabetes – This is a type of [diabetes] that can develop during pregnancy
- Cushing’s Syndrome – A disorder caused by too much cortisol in the body
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) – A condition that affects how a woman’s ovaries work
- Pancreatitis – Inflammation of the pancreas
Diabetes – Symptoms, Causes, and & Treatment
Symptoms of [diabetes] include:
- Frequent urination
- Thirst
- Hunger
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Erectile dysfunction in men
- Pain or numbness in the feet and hands
There are also some silent symptoms of diabetes that people might not know about:
- Blurred vision
- Feeling tired all the time
- Itchy skin
Preventing and Treating Diabetes
You can do some things to help prevent type-two [diabetes], including eating healthy foods, being active, and maintaining a healthy weight. If you have [diabetes], it is important to know the signs and symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) or high blood sugar (hyperglycemia).
You should also check your feet daily for blisters, sores, redness, swelling, tenderness, bumps/lumps on toes or legs. Treatment options include diet changes and exercise programs for those who get [diabetes] during childhood and adolescence.
Medication and insulin therapy are ideal for those who have type-one [diabetes]. The goal of treatment is to have blood sugar levels in a target range by balancing the amount of food you eat with exercise and sometimes other medicines or insulin. Examples of drugs used in the management of [diabetes] are sulfonylureas, meglitinides, biguanides, thiazolidinediones (TZDs), alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, and dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) inhibitors. For more information on the above, you can contact places like Tandem [Diabetes].