Phlebitis: Symptoms, Causes, Prevention: The phlebitis is inflammation of the vein walls. It often caused by the formation of blood clots inside it (thrombi). For this reason, it is also known as thrombophlebitis.
There are two types of phlebitis: superficial produced in a vein in the skin or deep vein thrombosis, located in the tissues under the skin. In the first case, it is usually a benign disease, and the prognosis is favorable. On the contrary, the second can become a severe problem involving a blood clot traveling to the lungs’ blood vessels, aggravating a pulmonary embolism. To get other information about the content you go through this what is street address.
Table of Contents
Prognosis of the disease
Deep vein thrombosis is a severe disease that, if left untreated, in many cases develops significant complications such as post-thrombotic syndrome or blood clots that travel to the lungs. Thus, deep vein thrombosis affects the quality of life of the patient and can be fatal.
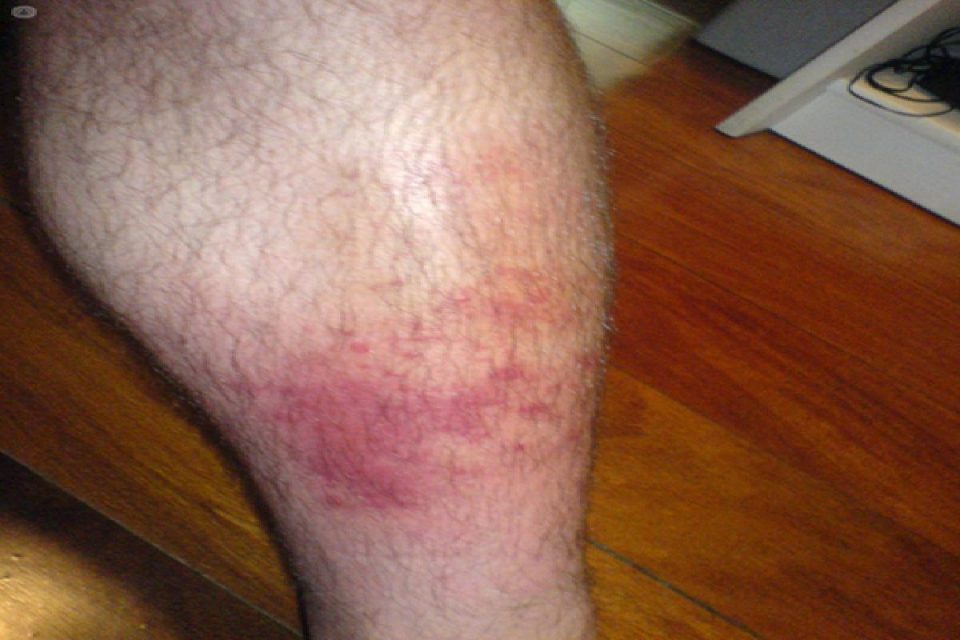
Symptoms of phlebitis
When it comes to slight phlebitis may not manifest symptoms. In deep vein thrombosis, common symptoms are:
- Pain and tenderness.
- Redness of the area (erythema).
- Bulging of the vein
- Slight fever.
What are the causes of phlebitis?
The most common causes of this disease are usually infectious diseases, but they can also be caused by trauma or a toxic trigger. The latter arise from an illness that can occur in a surgical act of any kind and location. In both traumatic and toxic ones, the existence of possible infection is presumed, and in postoperative ones.
Blood clots can form when a factor slows down the body or changes blood flow in the veins. Other conditions such as suffering from cancer, immune disorders such as lupus, smoking, being prone to blood clotting disorders, or taking estrogens or other birth control pills can induce the appearance of phlebitis.
Can it prevent?
The best way to prevent phlebitis and vascular problems is to take care of blood circulation.
In situations where there is no fluid flow of blood, it recommended to perform specific movements to facilitate it, such as taking long trips by car or plane or working long hours sitting or standing. It is advisable to walk or stretch your legs from time to time, drink plenty of fluids and wear rest stockings.
Treatments for phlebitis
Specific compression methods and wraps help decrease discomfort. The specialist may recommend analgesics, anticoagulants to prevent the appearance of new clots, especially in those cases of deep phlebitis, or thrombolytics to dissolve the existing clot.
Less common treatments are surgical removal of a vein near the surface or bypass of the injured vein itself.
The patient’s measures are to remove pressure from the affected area and thus reduce pain and the risk of worsening and lift the site to reduce inflammation.
What specialist treats it?
The angiologist and vascular surgeon is the specialist in treating venous pathologies. Thus, it will determine the diagnosis and perform a surgical treatment if necessary.