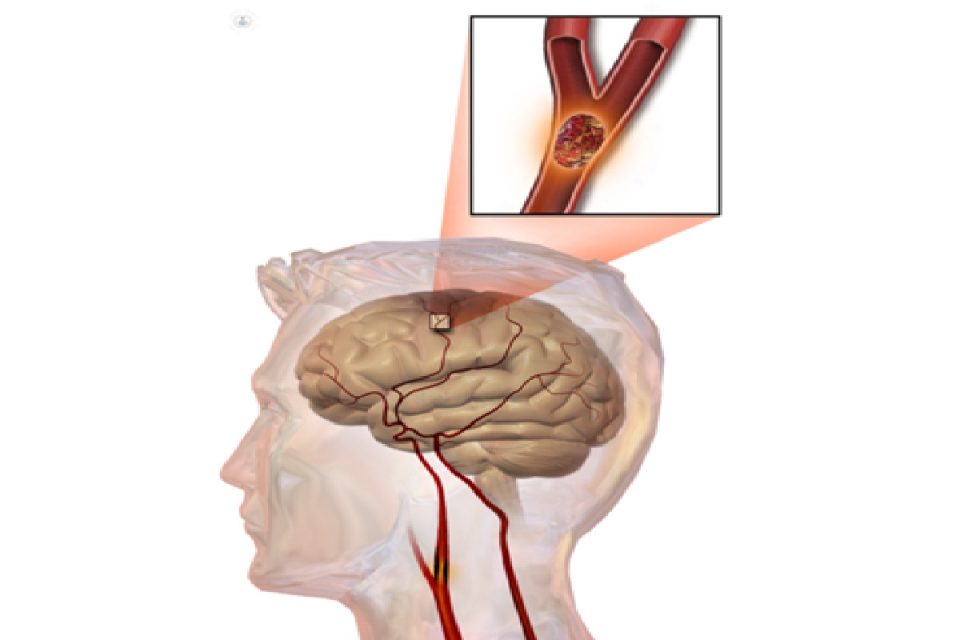
Stroke: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment Consist of?: Stroke understood to be the sudden interruption of cerebral circulation after injury to the blood vessels in this area. It usually occurs unexpectedly and can progress in a matter of minutes into major neurological syndromes.
The existing types of stroke are:
- Transient ischemic attack or TIA.
- Atherothrombotic stroke or thrombosis.
- Embolic stroke or embolism.
- Hemodynamic stroke.
- Hemorrhagic stroke.
Also read: Arterial Hypertension: Prognosis of The Disease
Table of Contents
What Symptoms Does it Present?
Symptoms that refer to stroke are often alarm signals and depend on the part of the brain where they occur. If it manifests in the left hemisphere, it can affect the expression or understanding of language, causing difficulty in speaking, mutism, substituting words or syllables, errors in the naming of objects, and problems reading and writing.
In the case of the right hemisphere, the patient may have a lack of recognition of the left side of the body or the environment, attention problems, frequent distractions, loss of concentration, poor credit of current or future conflicts, even without recognizing the disease itself and issues of behavior due to impulsivity or sudden character changes.
The symptoms in both cases are weakness or loss of sensation on the opposite side of the body and loss of image in the opposite visual field. In severe cases, coma or death can occur.For this and many other reasons, it is important for those who have suffered strokes to make sure their finances and end-of-life assurances, such as burial insurance, are in order
Causes of Stroke: Why it Occurs
Three primary forms of mechanisms of action are known: hemorrhagic ( arteriosclerosis and arterial hypertension are usually the most frequent causes); cerebral thrombosis, arteriosclerosis again being the most common cause; and, thirdly, cerebral embolism.
Can it be Prevented?
As with other pathologies, stroke prevention can eliminate risk factors, such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, from everyday life. In addition, high blood pressure and diabetes must controlled by a specialist.
Other risk factors can lead to stroke: maintaining high cholesterol levels, obesity, and suffering from certain heart conditions, such as arrhythmias or myocardial infarctions. The latter can cause blood clots that travel to the brain’s arteries, obstructing them and producing an ischemic stroke due to embolism.
What Does the Treatment Consist of?
Specialists always consider that strokes should treated in less than three hours by a team of neurologists to prevent complications. The first treatment applied is to inject anticoagulants to remove the clot or thrombus and allow normal blood flow.
In the event of bleeding, the patient may require interventional angiography or catheterization to repair the damaged artery through stents or by inserting a clip or staple into the bleeding aneurysm. In difficult situations where the patient’s life in danger, surgical catheter drainage allows blood to be expelled to the outside.